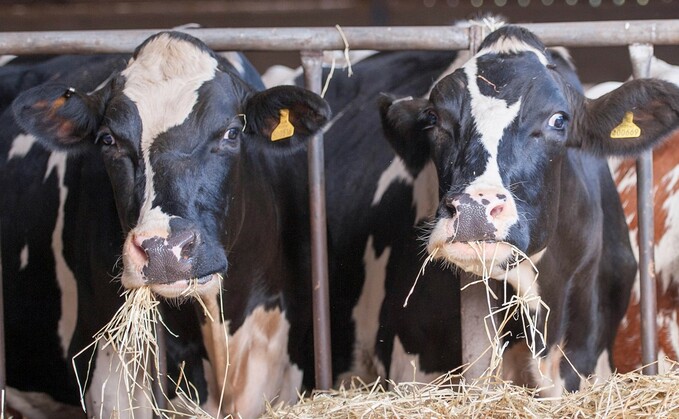
Livestock producers and growers supplying Morrisons are working towards reducing their carbon footprint after the retailer said their farm suppliers would be net zero by 2030. Emily Scaife finds out more about the ambitious plans and speaks to two farmers about their decision to take part in the scheme and what they hope to achieve.
As Morrisons strives to fulfil its pledge to be completely supplied by net zero carbon British farms by 2030, it is working with its suppliers to establish workable blueprints.
UK agriculture currently accounts for 10 per cent of all UK greenhouse gas emissions and the retailer is determined to meet this deadline, which is five years ahead of the market.
Sophie Throup, head of agriculture, fisheries and sustainable sourcing at Morrisons, says: "Our ‘Net Zero Agriculture' pledge is years ahead of industry expectations - and an ambitious target - but we see it as our duty to lead, support and encourage this.
"Ten years is not a long time and is probably still within most of our working lives.
It's on our watch to do something about it." About 40 farmers across all of Morrisons' direct farming supply chain areas are currently taking part in phase one of the project.
The retailer, together with a number of industry-leading experts and organisations, has begun the process of calculating the emissions produced on each farm.
The team will then be able to calculate the number of emissions the farmer would need to reduce or offset to get to net zero.
Sophie says: "We want all the farmers we work with directly to build their own paths to net zero farming, but within a set of principles which also govern good animal welfare and champion biodiversity as part of offsetting emissions produced.
"This shouldn't be an exclusive club, but one which every farmer, and therefore every customer, is able to access." The farm models will look at reducing carbon via rearing different animal breeds, using ow food-mile feedstuffs, using renewable energy and low emission housing and cutting down fuel and fertiliser use.
"They will also look to offset carbon emissions via planting grassland and clover, restoring peatland, improving soil health, planting trees and seeding hedgerows." Once a workable blueprint has been established, the models will be shared with all Morrisons farmers.
Sophie is hopeful they will be in a position to launch stage one of this in December 2021 at a conference for Morrisons farmers.
Beef farming is the most carbon-intensive form of agriculture, generating 45 per cent of carbon emissions for only 5 per cent of products sold.
Nearly half of this is down to methane produced by cattle.
So in addition, Morrisons will work with its beef farms to use smaller cattle breeds, pick low methane feeds and explore methane reducing supplements.
Spotlight Paul Coates, Barrackend Farm, Cumbria

If you're trying to reduce your costs, it is helping the environment at the same time.
It's all related." For Paul, running the farm and the environment go hand in hand.
He says: "We're very forwardthinking on the environment and efficient in what we're doing, which is why Morrisons approached us.
"We're in a Mid-Tier Stewardship scheme but we're planting hedgerows outside of that.
We didn't want to wait five years to get going so we're planting up to 400 metres of hedgerows every year.
As well as creating a nice habitat, it also provides shelter breaks for livestock.
"On the arable side, we used to plough everything, but we adopted a minimum tillage system three years ago, so now the plough is parked in the shed." This decision was made in order to help the farm's sandy soils retain moisture and organic matter.
Paul says: "It's paying dividends and has reduced our establishment costs by 50 per cent.
"Looking after the environment works for us - it either gives us a better return or reduces costs." Morrisons' team of experts is currently collecting data to help Paul decide on his next steps.
Paul says: "On the beef side, we're collecting daily weight gains and feed rations, which we hope to tweak and make more efficient.
"On the suckler cow side we're looking more at fertility so we can compress the carbon pattern and perhaps look at artificial insemination options.
"The biggest thing for us will be reducing imported proteins and using other options.
We currently use 70 per cent of home-grown produce in our feed.
We're trying to do as much as possible, but we're limited as to what we can grow on-farm."
Efficiency
Paul is determined to make the farm as efficient as possible and is not one to rest on his laurels.
He says: "There's always room for improvement; you're never finished.
What you do today could be totally different tomorrow, but we have to keep adapting."
Spotlight Tim Phipps, Bragborough Hall, Northamptonshire

We're doing lots of things in terms of biodiversity for the farm.
So, in theory, we should be in a good place, but I suspect still have a long way to go." The 344-hectare (850-acre) unit in Daventry currently runs 160 Stabiliser suckler cows and produces crops including winter wheat, winter barley and winter beans on a contract farming agreement.
The farm is also under a Countryside Stewardship agreement.
Tim, who runs the farm alongside his brother Louis and his parents, Geoff and Odette, is a huge advocate of employing sustainable approaches where possible across the business.
Tim says: "I've always been keen to lead the way in trying to be carbon neutral, because our long-term aim is to farm in as sustainable a way as we possibly can while still producing food." Tim and his family will work closely alongside Morrisons' farming and agriculture team and a range of industry leading experts from organisations such as RAFT Solutions and Harper Adams to trial projects and help further understanding of how beef farms can lower emissions and increase carbon offsetting.
He says: "At the moment we're trying to establish a baseline so we can see where we are in terms of our carbon footprint.
Once we have that we can make plans for what we could potentially do in the future."
Profitability
As part of the farm's Countryside Stewardship agreement, Tim is already growing conservation crops including wild bird covers, legume and clover-rich swards.
He says: "We've been growing clover for about five years and it seems to be making a really big difference in terms of soil structure.
We're able to make really good quality silage from it with high protein content, which is saving us from having to buy protein.
For the past five years our policy on-farm has been that we don't buy-in and use soya.
But if we can get away from buying-in any protein for our finishing ration then that would be good." Tim acknowledges that finding the balancing point between biodiversity and profitability is key for the business.
He says: "The clover is a good example of something which is good for carbon, but also good for our bank balance.
If we can save having to buy-in protein at a very high cost then it ticks a number of boxes." With the help of the team of experts, Tim hopes to explore a number key areas which contribute to emissions production on-farm, including considering the efficiency of different cattle breeds, fertility and feed, as well as manure and land management.
He says: "The more data I see, the further away from being carbon neutral I think we are, but that's good, as we need to know the exact scale of the challenge which lies in front of us."
FarmingCAN

Our FarmingCAN campaign, which we launched earlier this year, aims to educate consumers about farming all-year-round.
This year, as part of #Farm24, we aimed to connect farmers and consumers to show where their food comes from and educating them about what British farmers produce through our FarmingCAN social media channels.
With interest in food provenance and trust in British farmers, local produce, sustainability and the countryside, there has never been more of a prominent time to continue engaging with the public.










![Farming industry get behind FG's SAVE BRITAIN'S FAMILY FARMS campaign: "[This] campaign will help deliver our message to Government"](https://image.chitra.live/api/v1/wps/877bbe7/0f91ad70-ab9b-4ac9-bc2a-53dfa9e75558/10/BOB-Nigel-Owens-0848-Recovered-323x202.jpg)